This note describes how to use virt-manager on a x86-64 system and install an ARM or aarch64 operating system, namely Debian Linux.
Requirements
First install all requirements:
sudo apt install -y virt-manager qemu-kvm python-is-python3 guestfish
Enable and run libvirtd
sudo systemctl enable libvirtd
sudo systemctl start libvirtd
Add your user to the appropriate group
sudo usermod -a -G libvirt $USER
Best to reboot after this.
Debian Installation
We need the Debian DVD as it comes with all the components we are interested in. So get that from:
https://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current/armhf/iso-dvd/ or https://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/current/arm64/iso-dvd/
depending on what you want.
Once that is downloaded, we need the kernel vmlinuz and initrd.gz from the DVD, for that, mount the DVD.
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/disk
mount [DEBIAN IMAGE] /mnt/disk
cp /mnt/disk/install.a64/vmlinuz [wherever you want]
cp /mnt/disk/install.a64/initrd.gz [wherever you want]
Now, we’re ready to setup the machine.
- create a new VM and select the appropriate arch:
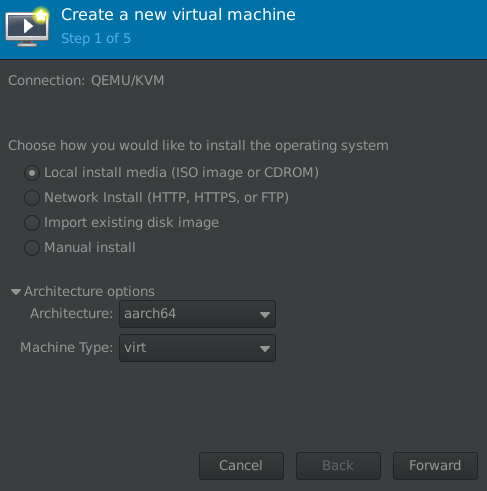
select the Debian DVD you downloaded on the next screen
setup the amount of CPUs and the RAM
setup the storage space you want
select
Customize configuration before install
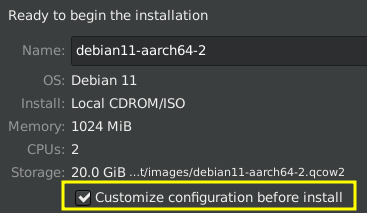
- apply the options below
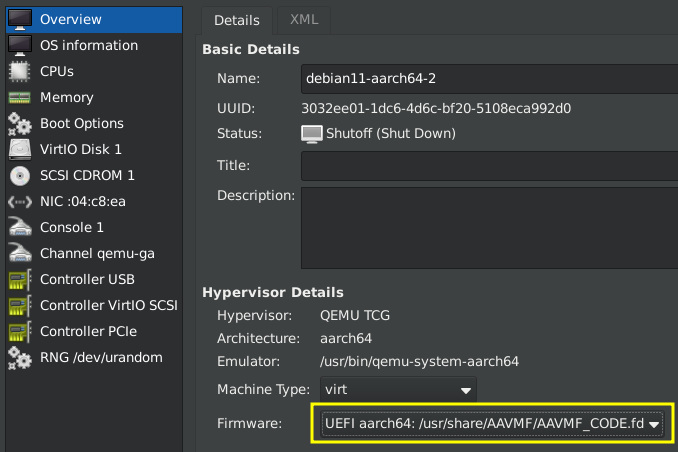
UEFI:
Direct kernel boot and Boot device order:
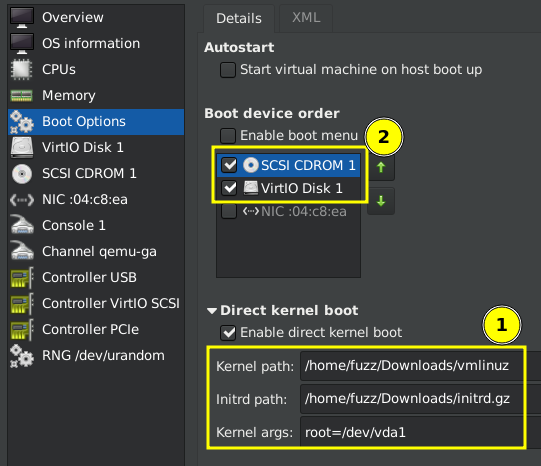
Remove the TPM by rightclicking and selecting Remove Hardware.
After you’ve got this, just begin the installation. You will get a screen with the Debian installer. Run the installer through but DO NOT REBOOT. Wait for this screen:
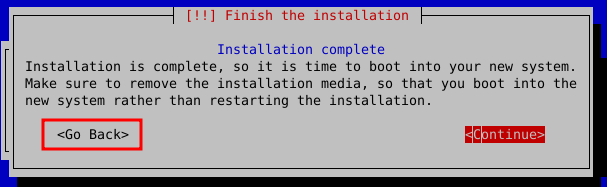
Choose Go Back here and scroll down in the menu, we want to Execute a shell, which will leave us with a command prompt after selecting this option.
First, do ip -a here to determine the IP of the VM, for me, it’s 192.168.122.35. Once you have that, do:
cd target/boot
ls -l
The two files we want are whatever the symlinks initrd./static and vmlinuz point to.
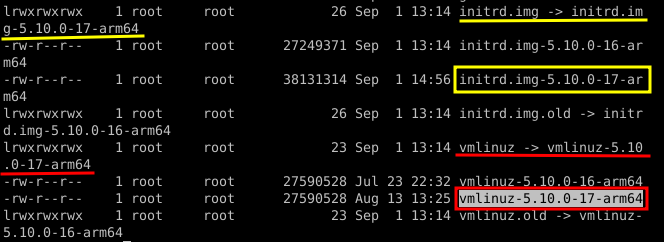
For this, we can use virt-copy-out like this:
sudo virt-copy-out -a [image] /boot/vmlinuz-5.10.0-17-arm64 .
sudo virt-copy-out -a [image] /boot/initrd./static-5.10.0-17-arm64 .
All we need for this is the location of the qcow2 image that was created by virt-manager. You can look this up in the VM information under the VirtIO Disk 1 - for me, it’s /var/lib/libvirt/images/debian11-aarch64.qcow2
Once these files are copied out, we can finish the installation in Debian by running exit from the shell.
Go to the Finish the installation step and reboot the machine. Here, you can just shut the guest off when the reboot is issued.
Now go back to the Boot Options in the VM settings and choose the two files we just copied from the VM, the Kernel vmlinuz and initrd. Also remove the CD so only the hard-disk is checked. In addition, the kernel args should be root=/dev/vda2 like this:
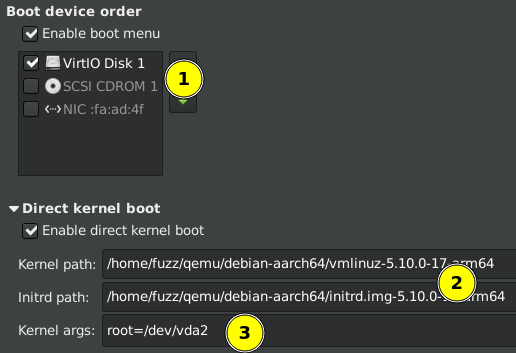
Now you can start the VM and enjoy your new Debian System.
PS: if you need a graphical user interface (you installed GNOME, XFCE, etc) just add a screen in the VM settings :)